알고리즘 Algorithm
[프로그래머스] Lv.2 배달 (다익스트라)
leexx
2023. 2. 18. 05:15
배달
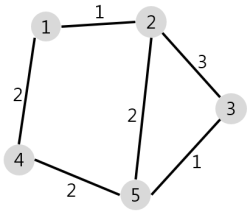
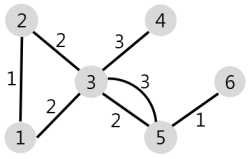
1번 node 에서 모든 node 로 이동할 때, cost K 보다 적게 이동할 수 있는 마을의 갯수를 구하는 문제이다.
한 점(1) 에서 모든 점으로 가는 cost 를 구하는 문제이며, cost 는 양수이므로 다익스트라 이다.
풀이
코드 구조
- 갈 수 있는 node 를 먼저 구한다. (candidates)
- 그리고 그 node 까지 갈 수 있는 path 들을 모두 구한다. (pq). 그리고 거기서 최단거리만을 뽑아 계산한다.
코드
let totalCost;
let adjacent;
let N;
function solution(n, roads, K) {
N = n;
totalCost = new Array(n);
adjacent = new Array(n);
// Infinity 로 초기화
totalCost.fill(Infinity);
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
adjacent[i] = new Array(N);
adjacent[i].fill(Infinity);
}
// adjacent 만들어둠
for (let i = 0; i < roads.length; i++) {
const [start, dest, c] = roads[i];
const minC = Math.min(adjacent[start - 1][dest - 1], adjacent[dest - 1][start - 1], c);
adjacent[start - 1][dest - 1] = minC; // 양방향의 cost가 같음
adjacent[dest - 1][start - 1] = minC; // 양방향의 cost가 같음
}
find();
return totalCost.filter((cost) => cost <= K).length;
}
function isPossible(path, i, adj, totalCost) {
if(adj[path][i] < Infinity) {
if(totalCost[i] > totalCost[path] + adj[path][i]) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
function find() {
const candidates = [];
const pq = new PriorityQueue();
// 0 에서 갈 수 있는 지점에 대해서 candidates 초기화
const startTown = 0;
totalCost[startTown] = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (adjacent[startTown][i] < Infinity) {
totalCost[i] = adjacent[startTown][i];
candidates.push(i); // 여기서는 q 써도 됨, 한 점 (0) 에서 다른 점 I 로 갈 수 있는 길은 하나만 있기 때문
}
}
while (candidates.length > 0) {
// [어떤 점 (node)] 에서 한 depth 에서 갈 수 있는 모든 [path 와 거기까지 가는데 걸리는 cost] 를 [구하기만] 한다. (가지 않는다. 구하기만 한다.)
while (candidates.length > 0) {
const node = candidates.pop();
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (isPossible(node, i, adjacent, totalCost)) { // node -> i 로 가도 되는지 체크
const accCost = totalCost[node] + adjacent[node][i];
const item = new Item(i, accCost);
pq.push(item);
}
}
}
const visit = new Set(); // 방문 체크용으로 쓰는 변수
// 위에서 구해둔 [갈 수 있는 path] 들 중에서 [최소한의 cost 를 갖는 path] 를 구한다.
while (pq.length() > 0) {
const {path, cost} = pq.pop();
if(!visit.has(path)) { // visit 했는지 check, 안했다면 방문함
visit.add(path);
totalCost[path] = cost; // updateTotalCost
candidates.push(path);
}
}
}
}
우선순위 큐 코드
더보기
function Item(path, cost) {
this.path = path;
this.cost = cost;
}
function PriorityQueue() {
this.array = [];
}
PriorityQueue.prototype.pop = function () {
this.array.sort(function (item1, item2) {
return item2.cost - item1.cost;
});
return this.array.pop();
}
PriorityQueue.prototype.push = function (item) {
this.array.push(item);
}
PriorityQueue.prototype.length = function () {
return this.array.length;
}
PriorityQueue.prototype.print = function () {
let ret = "";
for (let i = 0; i < this.array.length; i++) {
const {path, cost} = this.array[i];
ret += alpha[path] + "/" + cost + "...";
}
console.log(ret);
}