[프로그래머스] Lv.3 가장 먼 노드 (BFS) + 시간초과, 메모리초과 해결
가장 먼 노드
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
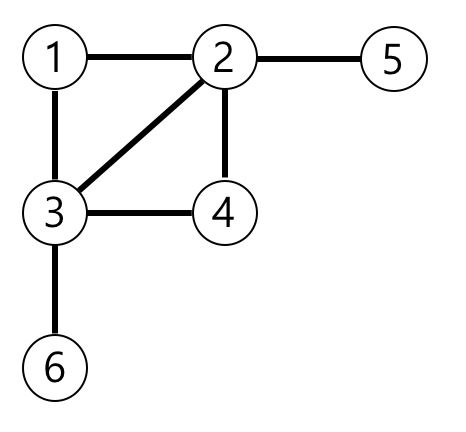
1번 node 에서 모든 node 로 가는 길이를 구한다. 이 때 모든 edge 의 가중치는 1이다.
즉 1 > 2 = 1 , 1 > 2 >5 = 3 , 1 > 3 > 6 = 3, ... 이다.
BFS인 이유
한 지점에서 갈 수 있는 위치 (동일 depth) 를 순차적으로 방문해야 한다. 따라서 가능한 경우의 수를 queue 에 쌓아서 동일 depth 에서 처리해줘야 한다.
[프로그래머스] Lv.2 게임 맵 최단거리 (BFS) + 반례 14개, 연습용 좌표판 PDF
게임 맵 최단거리 시작 지점부터 도착 지점까지 최단거리로 방문했을 때, 얼마나 걸리는지를 물어보는 문제이다. 예제의 경우 11 이다. 최단거리가 DFS 가 아닌 BFS 인 이유 한 지점에서 갈 수 있는
leexx.tistory.com
풀이
신경써야 하는 부분
이 문제에서는 N이 20,000 으로 꽤 크기 때문에 자칫하다간 메모리 에러, 시간초과가 난다.
인접 행렬은 인접 리스트로 구현
인접행렬은 N*N 으로 만드는거라 크기가 많이 크다. 예시의 경우 인접행렬은 이렇다.
[
[ Infinity, 1, 1, Infinity, Infinity, Infinity ],
[ 1, Infinity, 1, 1, Infinity, Infinity ],
[ 1, 1, Infinity, 1, Infinity, 1 ],
[ Infinity, 1, 1, Infinity, Infinity, Infinity ],
[ Infinity, Infinity, Infinity, Infinity, Infinity, Infinity ],
[ Infinity, Infinity, 1, Infinity, Infinity, Infinity ]
]N 이 최대 20,000 이면 20,000 * 20,000 해서 4억(...) 이 된다. 너무 크다. 그래서 인접 리스트를 사용했다.
인접리스트는 이렇다. 훨씬 작다.
{
'0': Set { 2, 1 },
'1': Set { 2, 0, 3, 4 },
'2': Set { 5, 3, 1, 0 },
'3': Set { 2, 1 },
'4': Set { 1 },
'5': Set { 2 }
}
중복이 되는 경우 없애기
candidates 를 다 돌면, candidates 에 temp 를 넣는다. (아래 코드) 이 때 temp 에 당연하게도 중복해서 node 가 들어갈 수 있다. 그래서 이 중복을 제거해주기 위해 Set 을 사용했다.
여기서 중복을 무시해도 되는 이유는, 한 depth 에서는 다음 node 로 갈 수 있는 최소한의 cost 를 갖는 방법은 단 하나이기 때문에, 중복을 무시해도 된다.
while (candidates.length > 0) { // O(N)
const node = candidates.shift();
cost[node] = Math.min(cost[node], step);
for (let adj of adjacent[node].values()) { // O(N)
if (cost[adj] == Infinity) {
temp.add(adj);
}
}
if (candidates.length == 0) {
candidates = [...temp];
temp = new Set();
step++;
}
}
코드
let N;
let adjacent;
let step = 1;
// N = n, 최대 20000
// M = edge length, 최대 50000
function solution(n, edge) {
let answer = 0;
N = n;
makeAdjacent(edge);
const cost = find();
// max 값인 애들만 출력
cost.sort((a, b) => b - a);
const maxCost = cost[0];
for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (cost[i] == maxCost) {
answer++;
} else {
return answer;
}
}
}
function makeAdjacent(edge) {
adjacent = {};
for (let i = 0; i < edge.length; i++) {
const [x, y] = edge[i];
if (adjacent[x - 1] === undefined) {
adjacent[x - 1] = new Set();
}
if (adjacent[y - 1] === undefined) {
adjacent[y - 1] = new Set();
}
adjacent[x - 1].add(y - 1);
adjacent[y - 1].add(x - 1);
// 1 -> 2, 3
// 2 -> 1, 3, 4, 5
// 3 -> 1, 2, 4, 6
// 4 -> 2, 3
// 5 -> 2
// 6 -> 3
}
}
function find() {
const cost = new Array(N);
let candidates = [];
let temp = new Set();
cost.fill(Infinity);
cost[0] = 0;
for (let adj of adjacent[0].values()) {
candidates.push(adj);
}
while (candidates.length > 0) { // O(N)
const node = candidates.shift();
cost[node] = Math.min(cost[node], step);
for (let adj of adjacent[node].values()) { // O(N)
if (cost[adj] == Infinity) {
temp.add(adj);
}
}
if (candidates.length == 0) {
candidates = [...temp];
temp = new Set();
step++;
}
}
return cost;
}